Reading sample:
Customs management
Companies need to have a process to manage importing goods into their country and the declarations that go along with importing. To improve efficiency, reduce costs in your compliance process, and avoid delays in customs clearance, you can automate your import declarations using functionality in SAP GTS.
Depending on the country, there may be multiple declarations required. For example, US Customs and Border Protection (CBP) has a rule as of January 26, 2009 called Importer Security Filing (ISF) and Additional Carrier Requirement. Under this rule, before any goods arrive by vessel into the US, the Importer Security Filing (ISF) needs to be submitted electronically, in advance, by the importer or the agent (licensed customs broker) to the CBP. This requirement only applies to cargo arriving in the US by ocean vessel, not to other modes of transportation. The ISF importer or its agent must provide eight data elements no later than 24 hours before the cargo is loaded on a vessel destined to the US. This declaration is required in addition to the standard customs import declaration, which applies to all modes.
ISF data elements are seller, buyer, importer of record number, consignee number, manufacturer (or supplier), ship-to party, country of origin, and the commodity’s Harmonized Tariff Schedule of the United States (HTSUS) number. Two additional data elements—container stuffing location and consolidator—must be submitted as early as possible and no later than 24 hours prior to the ship’s arrival at a US port.
CBP may issue liquidation of $5,000 per violation for the submission of an inaccurate, incomplete, or untimely filing. If goods for which an ISF has not been filed arrive in the US, the CBP can withhold the release or transfer of the cargo, refuse the unloading of the merchandise, or seize it if it is illegally unloaded. Additional noncompliant cargo could be subject to “do not load” orders at origin or further inspection on arrival.
From an import point of view, companies use different approaches to meet these requirements. We will discuss the import processes setup using SAP ERP Central Component (SAP ECC) and SAP GTS and the key configuration setup for building a robust solution, data, and process to support the requirement. We will also provide details on building an automated interface with your brokers for import declarations.
We will first provide a quick overview of the logistics integration and the process overview of import management. Import processes are triggered based on your incoming schedule, which could trigger based on the vendor purchase order. Let’s take the example of a purchase order logged in an SAP ECC system with the US as the country of destination. Go to either transaction ME22N (Change Purchase Order) or ME23N (Display Purchase Order) to see a purchase order with product GTS-N2 (see Figure 2.1).
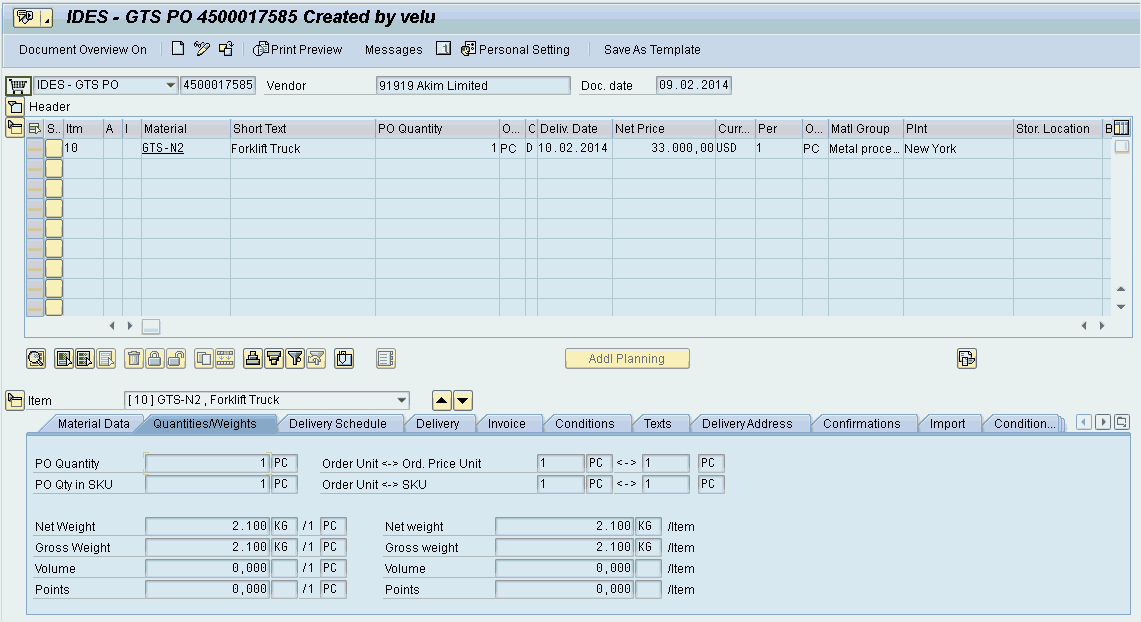
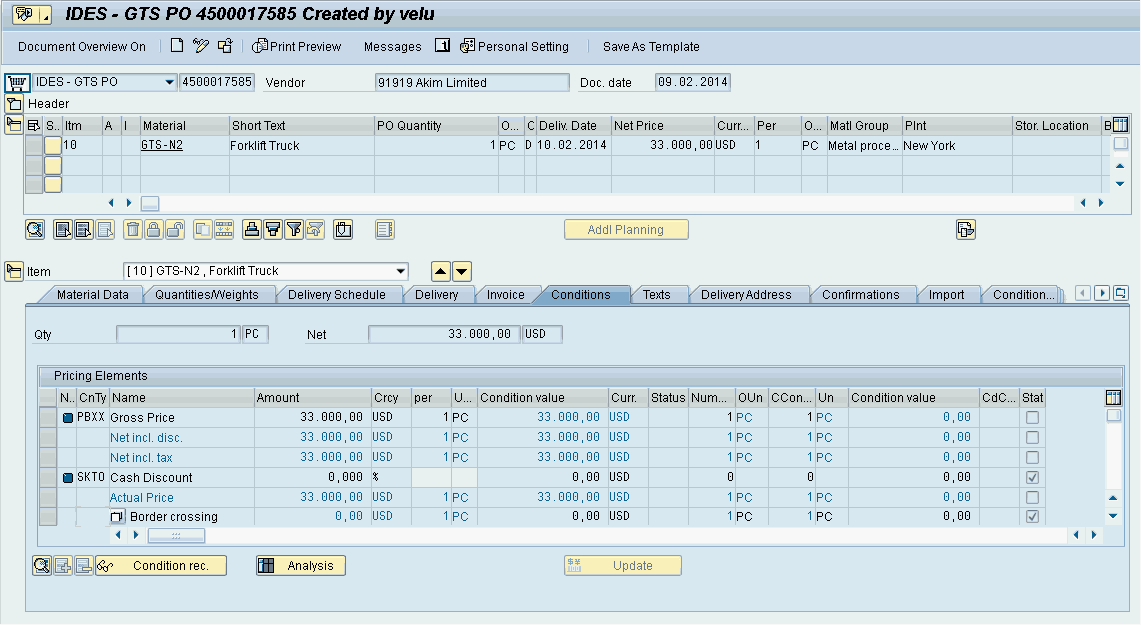
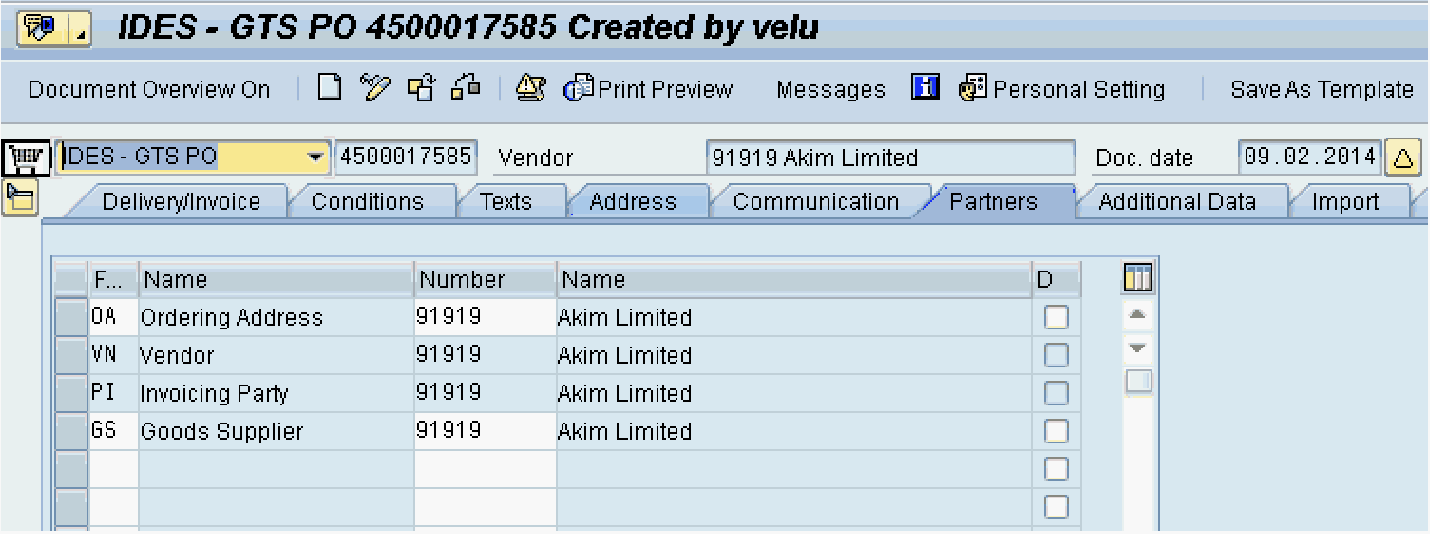
From the Display/Change Purchase Order screen, click on the Conditions tab to see the screen in Figure 2.2 and the Partners tab to see the screen in Figure 2.3. These screens provide the document data details that trigger the creation of a customs declaration document in SAP GTS: the purchase order, net value, and the statistical value. This chapter will review how to configure the communication between SAP ECC and SAP GTS, as well as tips for managing the SAP GTS Customs Declarations.
2.1 Customs declarations overview
2.1.1 Imports
SAP GTS has a document called a customs declaration. While they can be created manually in SAP GTS, the typical source is from purchase orders in SAP ECC.
As a purchase order is saved in SAP ECC (transaction ME21N), the information is automatically transferred to SAP GTS, and an equivalent customs declaration document is created in the system.
In SAP GTS, you can view these customs documents in transaction /SAPSLL/MENU_LEGAL, otherwise known as the SAP GTS Cockpit. From here, head to Customs Management • Import.
Figure 2.4 displays this screen, which allows you to generate the customs declaration worklist. Click execute (GTS - Preference and Customs Management) next to Enter Customs Declaration Prior To Goods Receipt.
Tags
- GTS
- SAP
- HANA
- SPL
- Compliance
Sign up for the newsletter and never miss any more news!
As a thank you, you will receive a 10% discount on a one-year license for our SAP learning platform.1
* Required
1. One-off and only for new customers. The voucher cannot be combined with other promotions and can only be redeemed at Espresso Tutorials GmbH.